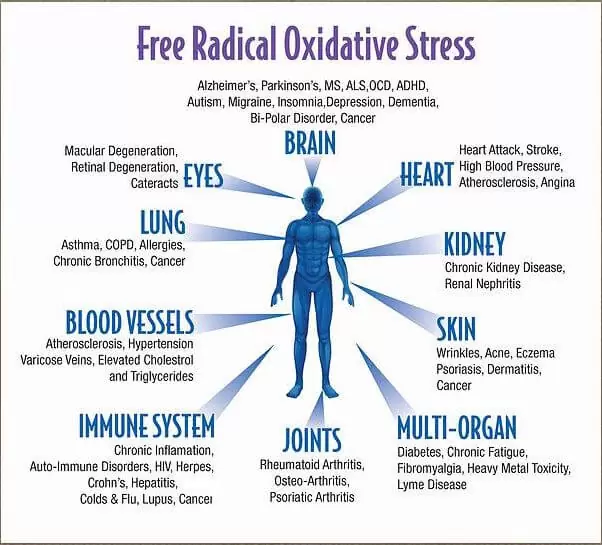
oxidative stress-free radical antioxidants
oxidative stress, the killer of healthy cells and
causative agent of aging What is oxidative stress?
A car’s engine produces energy after gasoline mixed with air is burned by a spark during this process, exhaust gases are released.
In our body cells the same thing actually happens, here are the mitochondria these are our biochemical motors.
Our nutrients burn by binding with oxygen (air from our lungs). At that moment our “exhaust gases” are created, these are our free radicals.
The healthy molecule has been turned into a harmful molecule because it lacks an electron. This free radical wants to steal an electron from the healthy molecules or weaken the healthy cells.
Antioxidants sacrifice themselves by giving an electron to the free radical and thereby neutralizing it.
If there are many more free radicals than antioxidants, there is oxidative stress.
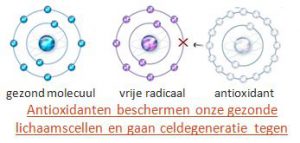
Someone with a lot of stress needs more antioxidants, or less stress……..
During intensive exercise, many free radicals also arise
Someone with a lot of stress and also intensive sports needs extra antioxidants
Virtually all of our formulas contain multiple antioxidants
- cell ageing (malfunctioning mitochondria)
- toxins (environmental pollution
- Food additives
- Medicines
- Tobacco smoke
- Alcohol
- heavy metals
- radiation (sunlight, X-rays, radiation from wireless and electrical equipment)
- physical exertion
- trauma, stress
- Infections
- Inflammation
- poor blood supply (ischemia)
- increased blood glucose levels
- obesity and overeating
- Flavonen (from citrus fruits, tea, herbs, peppers and celery)
- Isoflavones (from legumes, especially soy)
- Flavonols (including quercetin, from onions, broccoli and pears, for example)
- Anthocyanins (from grapes, cherries and berries)
- Proanthocyanidins (OPC) (from grape seeds and cocoa)
There is evidence that flavonoids have the following health effects in the body:
- Antioxidant effect: Flavonoids, especially those from citrus fruits, are antioxidants – which protect cells and tissue from damage– and promote the action of vitamin C. Conversely, vitamin C enhances the action of the flavonoids in citrus fruit.
- Flavonoids may have a beneficial effect on the condition of the heart and blood vessels.
- Flavonoids have a beneficial effect on the skin because they protect against free radicals and are good for blood vessels and connective tissue.
- Isoflavones, a certain type of flavonoids, help with transitional phenomena.
- Some flavonoids, especially OPC and quercetin, help with airborne pollen. They can reduce the release of histamine.
What suits you, what do you need?
You are interested but do not know which products suit you best?
Fill in the questionnaire and we will send you a free proposal by e-mail with a brief explanation.
Since 2000 we are practicing naturopathy. We will handle your information with utmost confidentiality in accordance with privacy legislation and NEVER share this information with third parties.

